
C1 Getting Started with C
S1 Hello World
Source Code
#include "stdio.h"
int main(void) {
puts("Hello, World!");
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
Headers :
- Function declarations
- Macros
- Data types
to use a function from standard library or from external library, you should include the header file of that library first.
int main(void)
The definition of a function:
- name of the function
- type of value that this function returns
- type and number of arguments it expects
voidmeaning none
{
}
A block of code begin and end.
puts("hello, world");
putsoutput text to standard output (the screen by default), followed by a new line."hello, world"is the string that will be written to the screen.- In C, every string literal value must be inside the double quotes “…”.
- every statement needs to be terminated by a semi-colon (i.e. ;).
return 0 :
- indicate that the program existed successfully.
Compiling Code
Using GCC
gcc hello.c -o hello
the compiler will create a binary file, the name of which is
given by the argument to the -o command line option (hello). This is the final executable file.
Using Clang
clang hello.c -o hello
C2 Comments
S1 Comments with preprocessor
#if 0
anything between here are ignored
#endif
S2 /* */ delimited comments
/* This is a comment */
/* This is a
multi-line
comment */
/*
* this is also
* multi line
* comment
*/
S3 // delimited comments
// this is a comment
// each of these
// are member of
// multi line
// comments
S4 Possible pitfall due to trigraphs
Pitfall:

Trigraph:
|  |
In c ??/ is a trigraph and is actually a longhand notation for \ . so we can’t have ??/ with in coment that may cause some error due to this.
// testing the trigraphs case. ??/
int main(void) {
int x = 20;
int foo = 20; // start at 20 ??/
int bar = 0;
bar += foo;
}
NOTE:
This did not cause any error in mac. May it cause some error on linux .
C3 Data Types
S1 Interpreting Declarations
- unary
*— a pointer — right to left — 2 (precedence) - binary
[]— an array — left to right — 1 - (1+n)-ary
()— a function — left to right — 1
*thing a pointer to …
thing[X] an array of size X of …
thing(t1,t2,t3) a function taking t1, t2, t3 and returning..
Examples:
char *names[20];
Precedence : [] 1, * 2
so, [] takes precedence over *, so the interpretation is :
Names is an array of size 20 of a pointer to char.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char *name;
return 0;
}

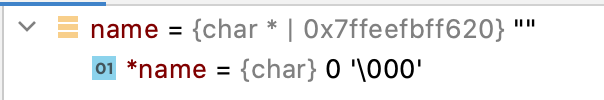
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char *name; // this is a pointer to char
char *names[20]; // this is an array that stores 20 pointers to chart
char (*place)[10]; // place is a pointer to array, of size 10 of char
int fn(long, short); // fn is a function which takes a long and a sort as argument and return int value
int *fn1(void); // () is procedure 1 so it is first. fn1 is a function which takes zero argument, and returns a pointer of int
return 0;
}
-
int (*fp)(void);— overriding the precedence of (); fp is a pointer to function which takes void arguments and returns int -
int arr[5][8]— multidimentional array.- [] — left to right
- arr is an array of size five which if an array of size 8
-
int **ptr;- two dereference operators have equal precedence.
int ptr;here ptr is a int variableint *ptr;here ptr is a pointer which points to an integerint **ptrhere ptr is a pointer which points to a pointer of int
-
int fn(void), *ptr, (*fp)(int), arr[10][20], num- fn is a function taking void and returning int
- ptr is a pointer to an int
- fp is a pointer to a function taking int and returning int
- arr is an array of size of an array of size 20 of int.
#include <stdio.h> int main() { /* * Subscripting "arr" and dereferencing it yields a "char" result. * Particularly: *arr[5] is of type "char". */ char *arr[20]; /* * Calling "fn" yields an "int" result. * Particularly: fn('b') is of type "int". */ int fn(char); /* * Dereferencing "fp" and then calling it yields an "int" result. * Particularly: (*fp)() is of type "int". */ int (*fp)(void); /* * Subscripting "strings" twice and dereferencing it yields a "char" result. * Particularly: *strings[5][15] is of type "char" */ char *strings[10][20]; return 0; }
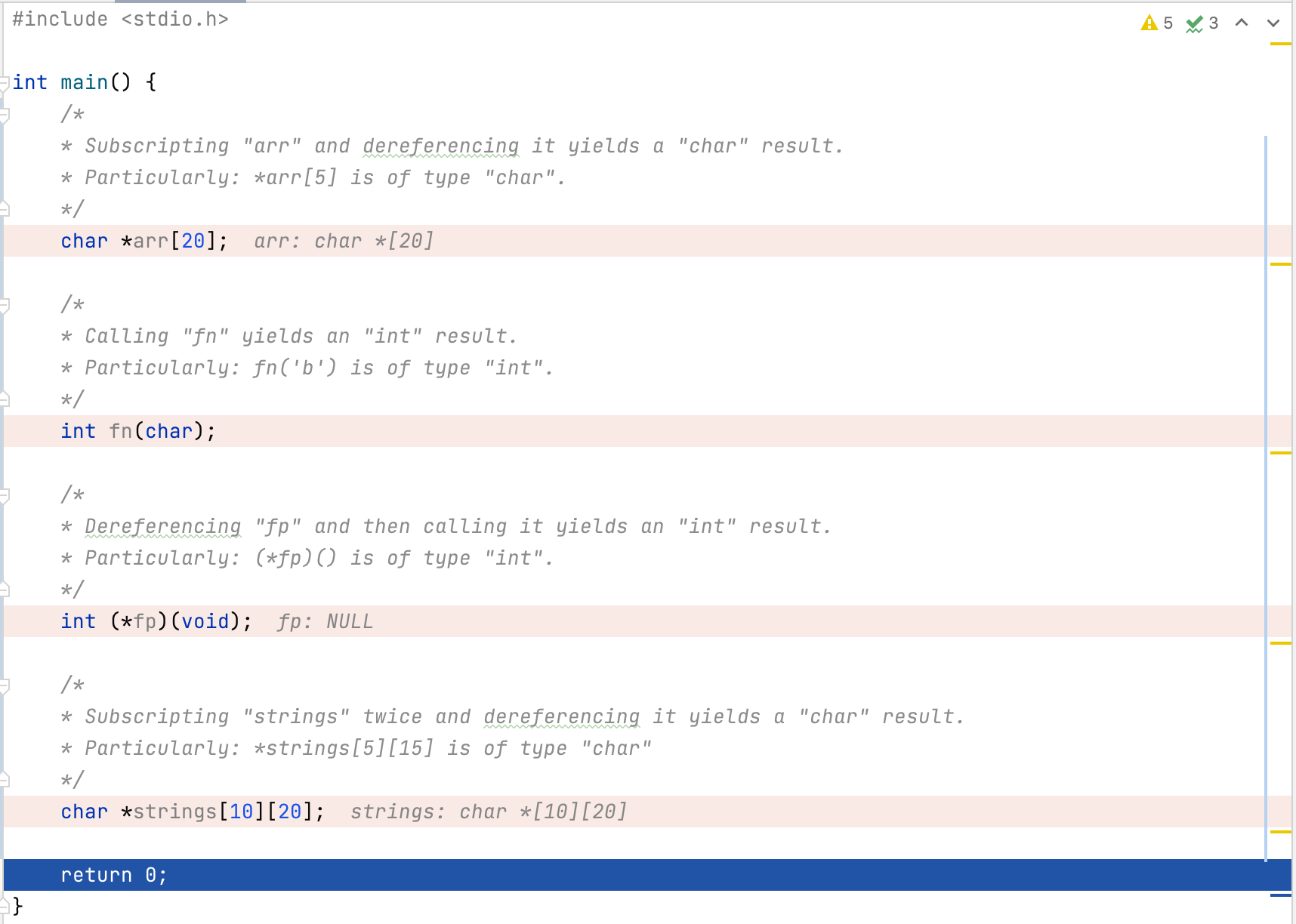
S2 Fixed Width Integer Types
The header <stdint.h> provides several fixed-width integer type definitions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
int main() {
// section 3.2 fixed width integer types
/* commonly used types includes */
uint8_t u8 = 255;
uint16_t u16 = 1024;
uint32_t u32 = 32;
uint64_t u64 = 65;
int64_t i64 = -65;
printf("%llx",u64);
printf("\n");
printf("%llx", i64);
return 0;
}
41
ffffffffffffffbf
S3 Integer types and constants
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
int main() {
// section 3.3
/*
* signed integers can be of these types the int after short or long is optional
*/
signed char c = 127; // required to be 1 byte
signed short int si = 32767; // required to be at least 16 bits -- 2 byte
signed int i = 32767; // required to be at least 16 bits -- 2 byte
signed long int li = 2147483647; // required to be at least 32 bits, 4 byte
signed long long int lli = 2147483647; // required to be at least 64 bits, 8 bytes
/*
* unsigned integers
*/
unsigned int ui = 65535;
unsigned short isi = 2767;
unsigned char uc = 255;
// For all types but char the signed version is assumed if the signed or unsigned part is omitted.
return 0;
}
- Decimal constants are always signed.
- Hexedecimal constants starts with 0x or 0X
- Octal constants starts just with a 0
Sufffix to describe width and signedness:
long int i = 0x32;// no suffix present int, or long intunsigned int ui = 65535u ;// u or U represents unsigned int, or long intlong int li = 655361;// l or L represent long int
The header file
| Macro | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| CHAR_BIT | smallest object that is not a bit-field (byte) | 8 |
| SCHAR_MIN | signed char | -127 / -(27 - 1) |
| SCHAR_MAX | signed char | +127 / 27 - 1 |
UCHAR_MAX unsigned char 255 / 28 - 1
CHAR_MIN char see below
CHAR_MAX char see below
SHRT_MIN short int -32767 / -(215 - 1)
SHRT_MAX short int +32767 / 215 - 1
USHRT_MAX unsigned short int 65535 / 216 - 1
INT_MIN int -32767 / -(215 - 1)
INT_MAX int +32767 / 215 - 1
UINT_MAX unsigned int 65535 / 216 - 1
LONG_MIN long int -2147483647 / -(231 - 1)
LONG_MAX long int +2147483647 / 231 - 1
ULONG_MAX unsigned long int 4294967295 / 232 - 1
Version ≥ C99
Macro Type Value
LLONG_MIN long long int -9223372036854775807 / -(263 - 1)
LLONG_MAX long long int +9223372036854775807 / 263 - 1
ULLONG_MAX unsigned long long int 18446744073709551615 / 264 - 1